Difference between revisions of "Unbalancers"
From #openttdcoop wiki
(→Unbalancer with Bypass) |
(Adjust size so its not interpolated) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Unbalancer with Bypass== | ==Unbalancer with Bypass== | ||
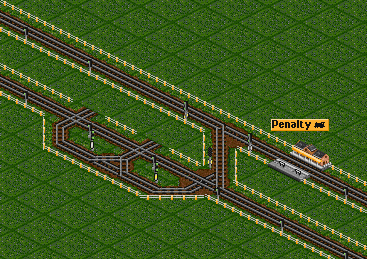
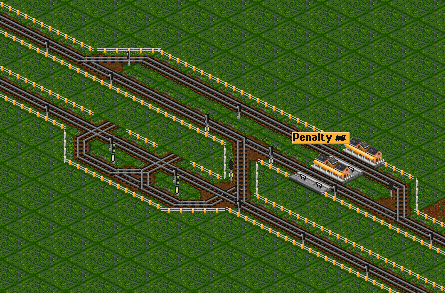
If a switching train is jammed and is blocking the upper track, a bypass is made. The bypass ensures the continuous flows of trains on the upper track. The bypass also needs a penalty station, else trains will use the bypass and not switch to the lower track. | If a switching train is jammed and is blocking the upper track, a bypass is made. The bypass ensures the continuous flows of trains on the upper track. The bypass also needs a penalty station, else trains will use the bypass and not switch to the lower track. | ||
| − | [[Image:Unbalancer_with_bypass.png| | + | [[Image:Unbalancer_with_bypass.png|445px|thumb|center|If a train stops in the branch, other trains can pass by using the bypass]] |
Revision as of 22:44, 28 July 2007
NOTE: This page is not final yet, so it might look messy and contain incorrect information.
Unbalancer
Overview
The Idea behind unbalancers is, that you want to keep the traffic on 1 lane while the second lane is as empty as possible. The principle is called SML.
Simple Unbalancer
To move trains onto one single lane, a track between them is made. To prevent trains switching tracks while a train is close to the switch, priority is added. To force the switching, a penalty is added to the track that has to be empty.
Unbalancer with Bypass
If a switching train is jammed and is blocking the upper track, a bypass is made. The bypass ensures the continuous flows of trains on the upper track. The bypass also needs a penalty station, else trains will use the bypass and not switch to the lower track.